- Pregnancy Care
- Normal Delivery
- Caesarean Section
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
- Ovulation Therapy
- Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) Treatment
- Menstrual Cycle Abnormality
- Hormonal Imbalance
- Infertility Treatment
- Family Planning
- Abortion Counselling
- Menopausal Problems
- Cervical Cancer Screening & Vaccination
- White Discharge
- Fibroid & Ovarian Cyst Treatment
Contact Us
Please feel free to contact us. We will get back to you. Or just call us now.
CALL US: +(91) 8591179577
MAIL US: swapnadahe07@gmail.com
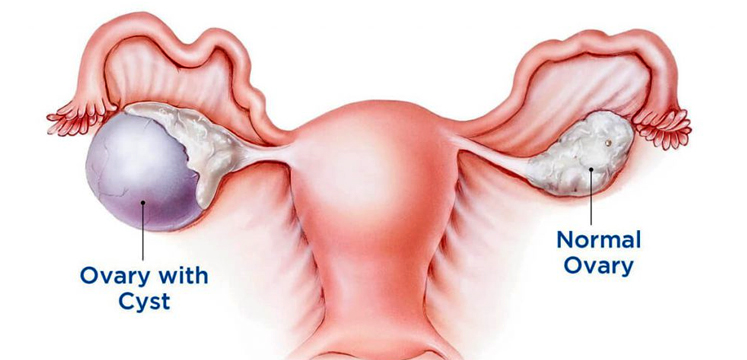
Fibroid & Ovarian Cyst Treatment
Fibroids and ovarian cysts are two common conditions that can affect women's reproductive health. While they may cause symptoms or complications in some cases, not all fibroids or ovarian cysts require treatment. The appropriate treatment options depend on the size, location, symptoms, and individual circumstances. Here's an overview of treatment options for fibroids and ovarian cysts:
-
Fibroids:
-
Watchful Waiting: If fibroids are small, asymptomatic, and not causing any complications, a "watch and wait" approach may be recommended. Regular monitoring through pelvic exams or imaging tests can be performed to track any changes.
-
Medications: Certain medications, such as hormonal contraceptives or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, can help manage symptoms associated with fibroids, such as heavy menstrual bleeding or pelvic pain. These medications do not eliminate fibroids but can provide temporary relief.
-
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Depending on the size, location, and symptoms, minimally invasive procedures can be considered. These include:
- Uterine artery embolization: This procedure blocks the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink and relieve symptoms.
- Myomectomy: It involves the surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus. Myomectomy is an option for women who wish to retain fertility.
- Hysteroscopic resection: Fibroids that protrude into the uterine cavity can be removed using a hysteroscope, a thin instrument inserted through the vagina and cervix.
-
Surgery: In cases of large or multiple fibroids, significant symptoms, or fertility concerns, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended. Hysterectomy is a definitive treatment but is only considered if other options have been exhausted or are not suitable.
-
-
Ovarian Cysts:
-
Watchful Waiting: Most ovarian cysts, especially small and functional ones, resolve on their own without treatment. In such cases, the doctor may recommend observation through regular monitoring and follow-up ultrasounds to ensure the cyst resolves.
-
Medications: Birth control pills or hormonal contraceptives may be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of new ovarian cysts. These medications can also help shrink existing cysts.
-
Minimally Invasive Surgery: If the cyst is large, causing persistent symptoms, or suspicious for malignancy, minimally invasive surgery may be recommended. Laparoscopic surgery can remove the cyst while preserving the ovary.
-
Surgical Intervention: In cases of larger or complex cysts, or if there is a suspicion of ovarian cancer, a more extensive surgical procedure, such as an oophorectomy (removal of the ovary) or a hysterectomy, may be necessary.
-
Treatment options for fibroids and ovarian cysts should be discussed with a healthcare professional, such as a gynecologist or reproductive health specialist. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms, desire for future fertility, size and location of the fibroids or cysts, and overall health considerations. The healthcare provider will assess the individual situation and recommend the most appropriate treatment approach.